Previous Years GATE Questions - Stress Distribution in Soil
1. The vertical stress at depth z, directly below the point load P is _____ (k is constant).
[GATE 1997: 1 Mark]
- kP / z
- kP / z3
- kP / z2
- kP / √z
Answer: Option C
Explanation:
Using Boussinesq's equation,
σz =
3P / 2Πz2
x 1 / { 1 + r2/z2}5/2σz = k
P / z2
Where, k - Boussinesq influence factor.
2. A point load of 700 kN is applied on the surface of thick layer of saturated clay. Using Boussinesq's elastic analysis, the estimated vertical stress (σv) at a depth of 2m and a radial distance of 1m from the point of application of the load is _____ .
[GATE 1998: 2 Marks]
- 47.5 kPa
- 47.6 kPa
- 47.7 kPa
- 47.8 kPa
Answer: Option D
Explanation:
Using Boussinesq's equation,
σz =
3Q / 2Πz2
x 1 / { 1 + r2/z2}5/2Here, Q = 700 kN, z = 2m, r = 1m.
Substituting the above values, σz = 47.8 kPa
3. A 25kN point load acts on the surface of an infinite elastic medium. The vertical pressure intensity in kN/m2 at a point 6m below and 4m away from the load will be _____ .
[GATE 2003: 1 Mark]
- 132
- 13.2
- 1.32
- 0.132
Answer: Option D
Explanation:
Using Boussinesq's equation,
σz =
3Q / 2Πz2
x 1 / { 1 + r2/z2}5/2Here, Q = 25 kN, z = 6m, r = 4m.
Substituting the above values, σz = 0.132 kN/m2
4. The vertical stress at some depth below the corner of a 2m x 3m rectangular footing due to a certain load intensity is 100 kN/m2. What will be the vertical stress in kN/m2 below the centre of a 4m x 6m rectangular footing at the same depth and the same load intensity?
[GATE 2007: 1 Mark]
- 25
- 100
- 200
- 400
Answer: Option D
Explanation:
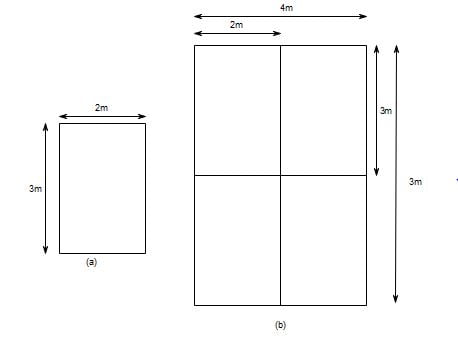
Considering Fig (a), given that the vertical stress at some depth below the corner due to certain load intensity is 100 kN/m2
Now, For Fig (b), the vertical stress at the centre of 4m x 6m footing due to the same load = Sum of vertical stress below the corner of all 2m x 3m footing
⇒ The vertical stress at the centre of 4m x 6m footing due to the same load = 4 x 100 = 400kN/m2
5. A footing 2m x 1m exerts a uniform pressure of 150 kN/m2 on the soil. Assuming a load dispersion of 2 vertical to 1 horizontal, the average vertical stress (kN/m2) at 1m below the footing is _____ .
[GATE 2008: 2 Marks]
- 50
- 75
- 80
- 100
Answer: Option A
Explanation:
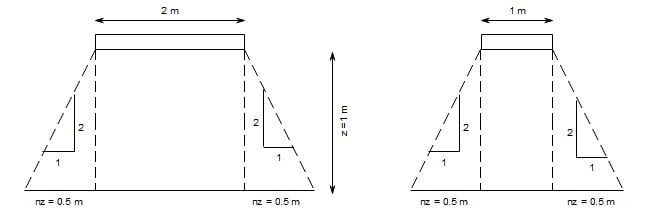
As the load dispersion is 2 vertical to 1 horizontal, n =
1 / 2
Average vertical stress, σz =
Q x LB / (L + 2nz)(B+2nz)
Here, z = 1m,= L = 2m, B = 1m, Q = 150 kN/m2
Average vertical stress, σz =
150 x 2 x 1 / (2 + 1)(1 + 1)
= 300 / 6
= 50 kN/m26. The vertical stress at point P1 due to the point load Q on the ground surface as shown in figure is σz. According to Boussinesq's equation, the vertical stress at the point P2 shown in figure will be _____ .
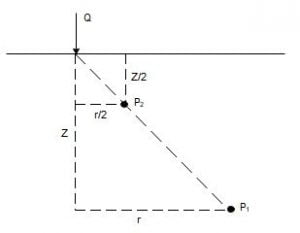
[GATE 2010: 2 Marks]
- σz/2
- σz
- 2σz
- 4σz
Answer: Option D
Explanation:
According to Boussinesq's equation,
σz =
3Q / 2Πz2
x 1 / { 1 + r2/z2}5/2When r = r/2 and z = z/2,
Vertical stress =
3Q / 2Π(z/2)2
x 1 / { 1 + (r/2)2/(z/2)2}5/2⇒ Vertical stress = 4σz
7. A uniformly disturbed line load of 500 kN/m is acting on the ground surface. Based on Boussinesq's theory, the ratio of vertical stress at depth 2m to that at 4m, right below the line of loading, is _____ .
[GATE 2017: 1 Mark, I Set]
- 0.25
- 0.5
- 2.0
- 4.0
Answer: Option C
Explanation:
Boussinesq's Equation for line load, σz =
2q / Πz
x 1 / { 1 + x2/z2}2 Here, q= 500 kN/m
Below the line load, x = 0
Thus, σz ∝
1 / z
Now,
σz @2m / σz @4m
= 1/2 / 1/4
= 4 / 2
= 2 Thus, the ratio of vertical stress at depth 2m to that at 4m, right below the line of loading is 2.
8. Consider a square-headed area ABCD on the ground with its centre at M as shown in the figure. Four concentrated vertical loads of P = 5000 kN are applied on this area, one at each corner. The vertical stress increment (in kPa, upto one decimal place) due to these loads according to the Boussinesq's equation , at a point 5m right below M is _____ .

[GATE 2017: 2 Marks, II Set]
Answer: 190.8
Explanation:
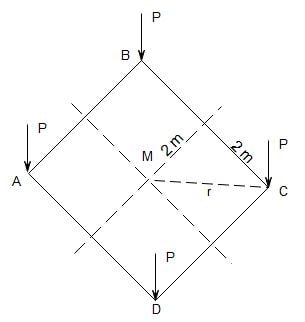
Here, P = 5000 kN, z = 5m and r = √(22 + 22) = 2√2 m
Using Boussinesq's equation,
σz =
3Q / 2Πz2
x 1 / { 1 + r2/z2}5/2Here, Q = P = 5000 kN.
Substituting the known values of Q, z and r, σz = 190.8 kPa.
9. Which one of the following statements is NOT correct?
[GATE 2018: 1 Mark, II Set]
- When the water content of soil lies between its liquid limit and plastic limit, the soil is said to be in plastic limit.
- Boussinesq’s theory is used for the analysis of stratified soil.
- The inclination of stable slope in cohesive soil can be greater than its angle of internal friction.
- For saturated dense fine sand, after applying overburden correction, if the Standard Penetration test value exceeds 15, dilatancy correction is to be applied.
Answer: Option B
Explanation:
Boussinesq's theory is based on the assumption that the soil is homogeneous and isotropic. Hence, it can not be applied for stratified soil.
10. In a soil specimen, the total stress, effective stress, hydraulic gradient and critical hydraulic gradient are σ, σ′, i and ic respectively. For initiation of quicksand condition, which one of the following statements are TRUE?
[GATE 2019: 1 Mark, I Set]
- σ′ = 0 and i = ic
- σ′ ≠ 0 and i = ic
- σ = 0 and i = ic
- σ′ ≠ 0 and i ≠ ic
Answer: Option A
Explanation:
Necessary condition for Quicksand condition is
i) Effective stress, σ′ = 0
ii) Hydraulic gradient, i = Critical Hydraulic gradient, ic

